Baidu: China’s Search Engine Giant

The Chinese search engine market is a unique landscape, distinct from the rest of the world. With Google blocked, Baidu has emerged as the dominant search engine, capturing a significant portion of the market. For businesses aiming to succeed in China, understanding and optimising Baidu’s search engine is essential.
Baidu: The “Google of China”
Often referred to as the “Google of China,” Baidu is the primary search engine used by millions of Chinese internet users. Its dominance is rooted in its ability to provide localised, Mandarin-friendly search results and services. To effectively reach and engage the Chinese audience, businesses must navigate Baidu’s ecosystem, which includes its search engine, advertising platform, and content distribution channels.
This blog explores the nuances of advertising, content, and website strategies in Baidu’s ecosystem.
Key Features
- Search Algorithm and Indexing: Baidu’s web crawler, Baiduspider, meticulously scours websites worldwide, constantly expanding its massive database by cataloguing webpages across the internet. Its complex ranking formula prioritises results based on relevance, quality, and user engagement, specifically tailored for Mandarin and user actions. However, unlike its Western counterpart Google, Baidu’s exact formula remains a closely guarded secret.
- User Interface and Experience:
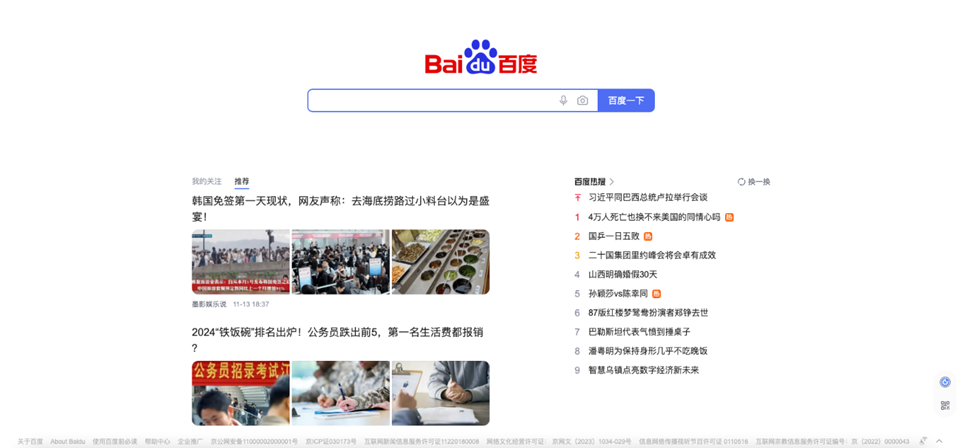
- Homepage – Baidu’s homepage maintains a simple search bar much like Google, and also features shortcuts to trending sections like news, images, videos, maps, and additional services.
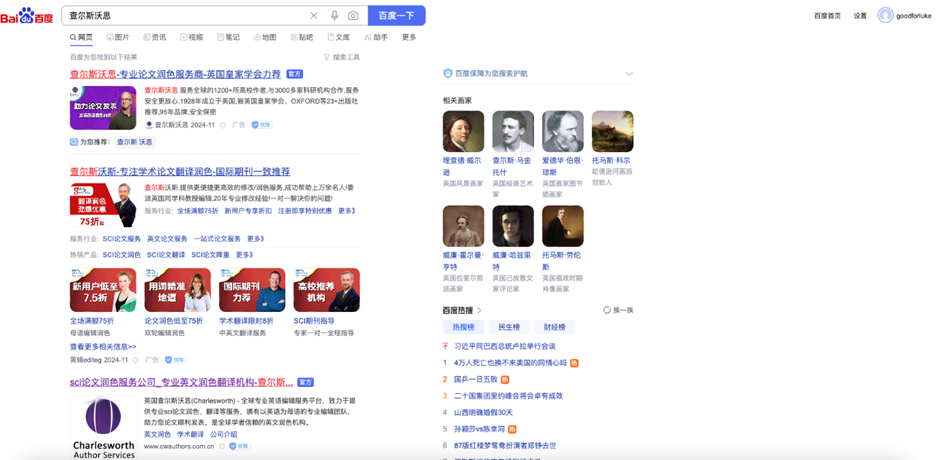
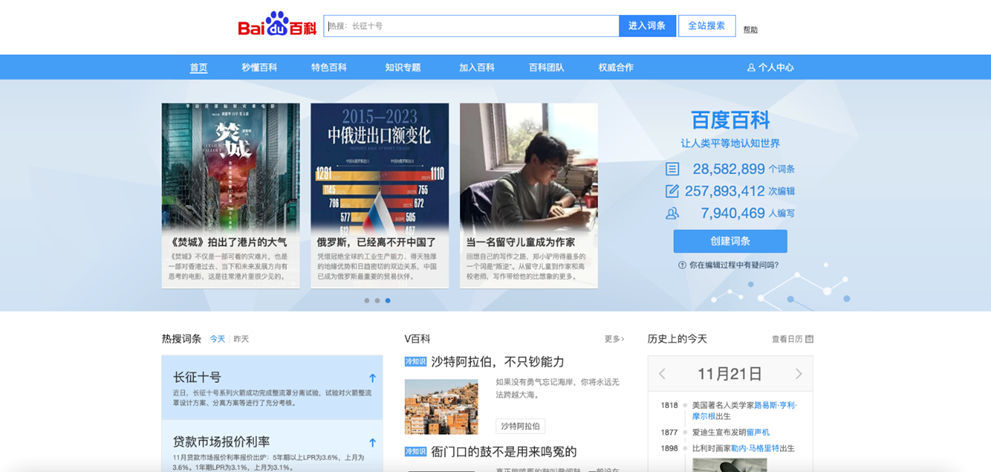
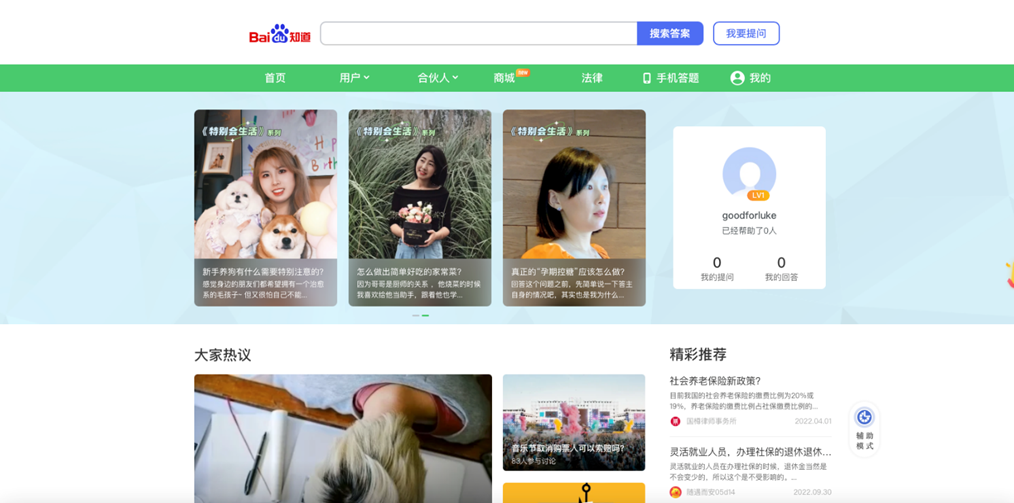
- Search Results – A fusion of natural listings, paid advertisements, and supplementary highlights like Baidu Knows (a Q&A platform), Baidu Baike (a Wikipedia-style database), and multimedia files populate the results page.
Baidu Baike
Baidu Knows
The Importance of Baidu Ads
Open Baidu’s home page and one thing is clear: ads are everywhere. Paid search ads can take up to 60% of the screen. This means if your site isn’t ranking at the top organically, chances are your audience will never scroll far enough to find it. On Baidu, being on page two is as good as being invisible.
For businesses, this is a wake-up call: if you want visibility, you’ve got to invest in ads. Unlike Google, where strong SEO might suffice, Baidu’s landscape demands you pay to play. It’s not just about exposure either—Chinese users often see paid ads as more credible. A solid Baidu Ads campaign can put your business front and centre, driving both clicks and trust.
The Language Advantage: Mandarin Matters
If you think your English-language content will cut it in China, think again. Baidu is designed for a Mandarin-speaking audience, and the algorithm strongly favours local language content.
Here’s why:
- Chinese users prefer searching in Mandarin, even for global brands.
- Baidu loves exact-match keywords, so having the right Mandarin phrases in your content is critical.
- Localisation isn’t just about language—it’s about understanding cultural nuances. A literal translation won’t do the trick; your content needs to feel relevant to Chinese readers.
If you’re serious about reaching your audience, translating your website and tailoring it for the local market is non-negotiable.
Your Website: Does Domain and Hosting Matter?
When it comes to getting your website noticed on Baidu, it’s not just about content. The domain name and hosting location can make or break your success. Let’s explore the options.
Mandarin Content on .com Domains
If you have already got a .com domain, don’t worry—you can still rank on Baidu as long as your site is optimised for Mandarin. But there’s a catch:
- Trust Issues: Chinese users often trust .cn domains more. They see .cn as local and reliable.
- SEO Impact: Baidu’s algorithm tends to give a slight edge to .cn domains for local searches.
While a .com domain is fine for global credibility, consider registering a .cn domain if you’re serious about building trust in China.
To .cn or Not to .cn?
Using a .cn domain comes with perks, but it’s not all smooth sailing:
- Pros:
- It signals you’re a local player, boosting trust.
- It might help you rank higher in Baidu searches.
- Cons:
- You will need a Chinese business entity to register it.
- The paperwork can be a hassle.
Hosting in China: Why It Matters
Speed is everything online, and this is especially true in China. Hosting your website outside the country means your site has to navigate the Great Firewall, which can slow things down to a crawl. Hosting in China ensures faster load times for local users, but there’s a catch:
- You will need an ICP license, and a government permit to host your site in China.
- The licensing process can be complex but is essential for serious players.
If hosting in China feels like too much of a leap, you can use a Content Delivery Network (CDN) with servers in Asia to speed things up. However, this is only a partial fix and won’t completely bypass the Firewall.
Advertising
Paid Placement – Baidu’s primary revenue originates from its advertising marketplace Baidu Tuiguang, enabling businesses to bid on keywords and display ads within organic listings.
Display Ads – Baidu also offers display advertising distributed across its vast network of websites and apps.
Importance in Chinese Digital Marketing
- Market Dominance – Baidu retains an overwhelming share of China’s search engine sector, making it crucial for digital marketing and search engine optimisation targeting Chinese consumers.
- Advertising Reach – With its extensive advertising network and specialised services, Baidu provides multiple touchpoints for businesses to engage their target audience.
Difference Between Google Ads and Baidu Ads
It’s important to note that Google is banned in China. Therefore, the choice between Google Ads and Baidu Ads is not a direct comparison. While Google Ads is a powerful tool for global marketing, Baidu Ads is the primary platform for reaching Chinese consumers.
Difference between Google Ads and Baidu Ads, key factors to consider:
- Target Audience: Consider the geographic location and language preferences of your target audience. Google dominates globally with English searches, while Baidu reigns supreme in China with Mandarin searches.
- User Characteristics: Google users tend to have a broader international perspective, while Baidu users primarily search for Chinese-related topics.
- Advertising Formats: Google Ads offers a wider range of advertising formats, including search ads, display banners, and video ads. Baidu primarily focuses on search ads.
- Targeting Accuracy: Google Ads generally offers more precise user targeting based on various factors, potentially leading to higher conversion rates. Baidu relies more heavily on keyword targeting.
- Price Competition: Both platforms involve competitive bidding. While Google Ads might present higher costs for certain keywords depending on the location and competition, Baidu can also be price-competitive.
Conclusion
By understanding the unique characteristics of Baidu and its role in the Chinese digital landscape, businesses can effectively leverage Baidu Ads to reach and engage their target audience. If you’re looking to expand your marketing efforts into China, Baidu Ads is a crucial tool to consider.
Ready to take your China digital marketing strategy to the next level? Let our team of experts help you navigate the complexities of Baidu Ads and craft a winning campaign. Contact us today for a free consultation!


